Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 7 Understand The Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem
Page 387 Exercise 2 Answer
The Pythagorean equation states that if the lengths of any two sides are known the length of the third side can be calculated using
(hypotenuse)2 = (base)2 + (perpendicular)2
It relates the sides of a right triangle in a simple way.
So if the lengths of sides satisfies this, it is a right angled triangle.
If the sides satisfy
(hypotenuse)2 = (base)2 + (perpendicular)2, then it is right angled triangle.
Page 387 Focus On Math Practices Answer
The Pythagorean equation states that if the lengths of any two sides are known the length of the third side can be calculated using
(hypotenuse)2 = (base)2 + (perpendicular)2
It relates the sides of a right triangle in a simple way.
So if the lengths of sides satisfies this, it is a right angled triangle.
Therefore, Kayla can use the straws that form a right triangle to make a triangle that is not a right triangle.
Kayla can use the straws that form a right triangle to make a triangle that is not a right triangle.

Envision Math Grade 8 Chapter 7 Solutions
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 388 Essential Question Answer
The Pythagorean equation states that if the lengths of any two sides are known the length of the third side can be calculated using
(hypotenuse)2 = (base)2 + (perpendicular)2
It relates the sides of a right triangle in a simple way.
So if the lengths of sides satisfies this, it is a right angled triangle.
If the sides satisfy (hypotenuse)2 = (base)2 + (perpendicular)2
then the triangle is right angled.
Page 388 Convince Me Answer
Given: Right angled triangle
To prove :Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
We will write the converse of Pythagoras theorem and justify it.
The converse of the Pythagorean Theorem:
A triangle in which the sum of the square of the length of two sides is equal to the square of the length of the third side is a right triangle.
That means in a triangle ABC we have AC2 = AB2 + BC2
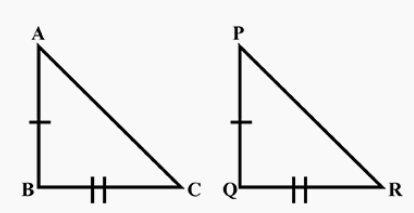
To prove: ∠B = 90°
Let us construct another triangle PQR as shown

By SSS congruency we have ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
Using ‘corresponding sides of congruent parts are similar’ we get ∠B = 90°
Hence converse of Pythagoras theorem is proved.
Page 389 Try It Answer
Given: A triangle with sides 10,√205,√105 feet
To find: whether the triangle is right angled or not.
We will use the Pythagoras formula and verify it.
If the sides satisfy (hypotenuse)2 = (base)2 + (perpendicular)2
then the triangle is right angled.
By the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem:

The formed triangle is a right angled.
Given lengths form right angled triangle.
Envision Math Grade 8 Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Answers
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 390 Exercise 1 Answer
If the triangle is a right triangle, the hypotenuse is its longest side.
Compare side lengths 10,√205,√105
Check if the lengths c = √205,
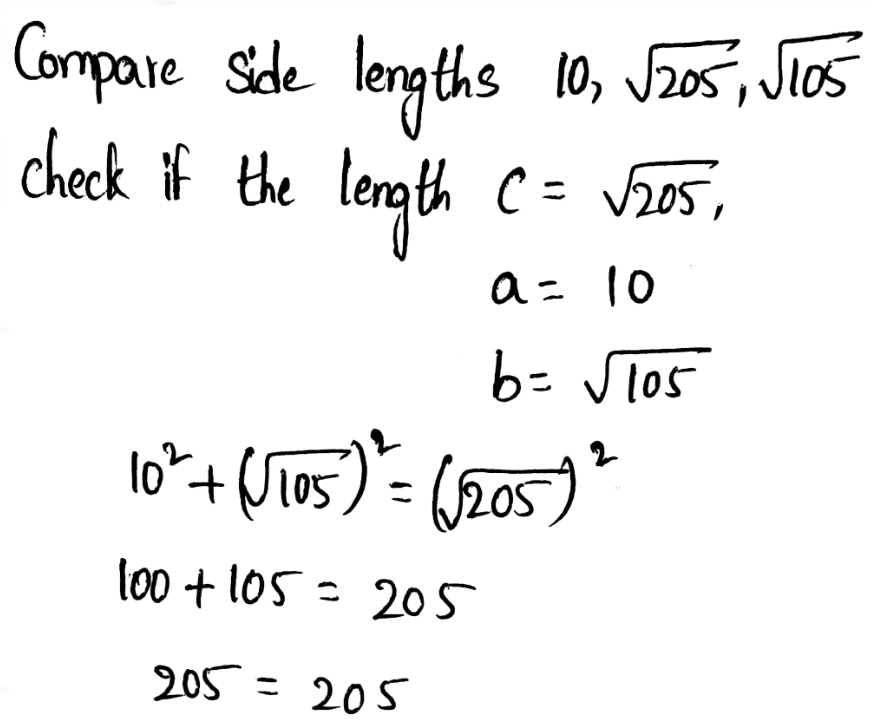
The triangle is a right triangle by the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.
Page 390 Exercise 3 Answer
The formula for the Pythagorean Theorem is: a2 + b2= c2
The first component that can easily be substituted in the equation is the hypotenuse, which is the longest side of the right triangle. If the hypotenuse is already determined, the remaining values of the side lengths can be substituted in any of the remaining variables in the equation a,b.
Keep in mind that other variables can be used other than a,b, and c.
For example, a right triangle has side lengths of x = 4,
y = 5
z = 3
So, we have
a2 + b2= c2
Hence, the longest side of the triangle is to be substituted on the right side of the equation, while the remaining two side lengths are to be substituted on the left side of the equation.
Page 390 Exercise 4 Answer
Given:
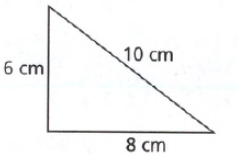
To determine the given triangle is a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


Both sides are equal
So, the triangle is the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is the right angle triangle.
Page 390 Exercise 5 Answer
Given:
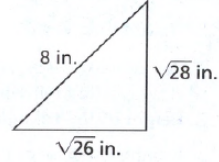
To determine the given triangle is a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


So, the triangle is not the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is not the right angle triangle.
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Student Edition Solutions Chapter 7
Page 390 Exercise 6 Answer
Given:
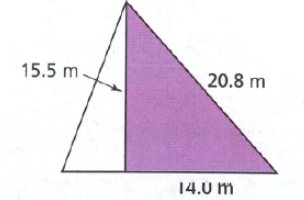
To determine the given triangle is a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


So, the triangle is not the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is not the right-angle triangle.
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 391 Exercise 7 Answer
Given:
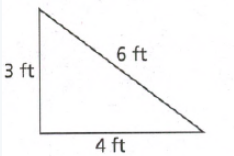
To determine the given triangle is a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


So, the triangle is not the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is not the right angle triangle.
Page 391 Exercise 8 Answer
Given:
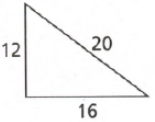
To determine the given triangle is a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


So, the triangle is the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is the right angle triangle.
Envision Math Exercise 7.1 Answers Grade 8
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 391 Exercise 9 Answer
Given:
Length of the triangle 5, 15, and √250.
To determine the given sides form a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have.

Hence, the given triangle is the right angle triangle.
Page 391 Exercise 10 Answer
Given:
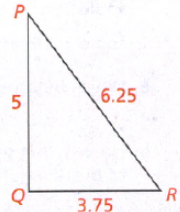
To determine the given sides form a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


So, the triangle is the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is the right angle triangle.
Page 391 Exercise 11 Answer
Given:
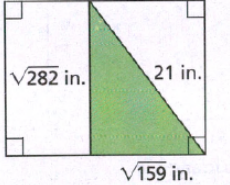
To determine the given sides form a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,


So, the triangle is the right triangle.
Hence, the given triangle is the right angle triangle.
Page 391 Exercise 12 Answer
Given:
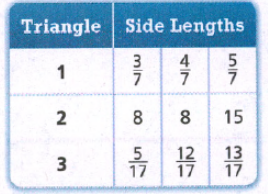
To determine the given sides form a right triangle or not.
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
First, check for triangle 1.

So, the triangle is the right triangle.
Now, check for triangle 2.
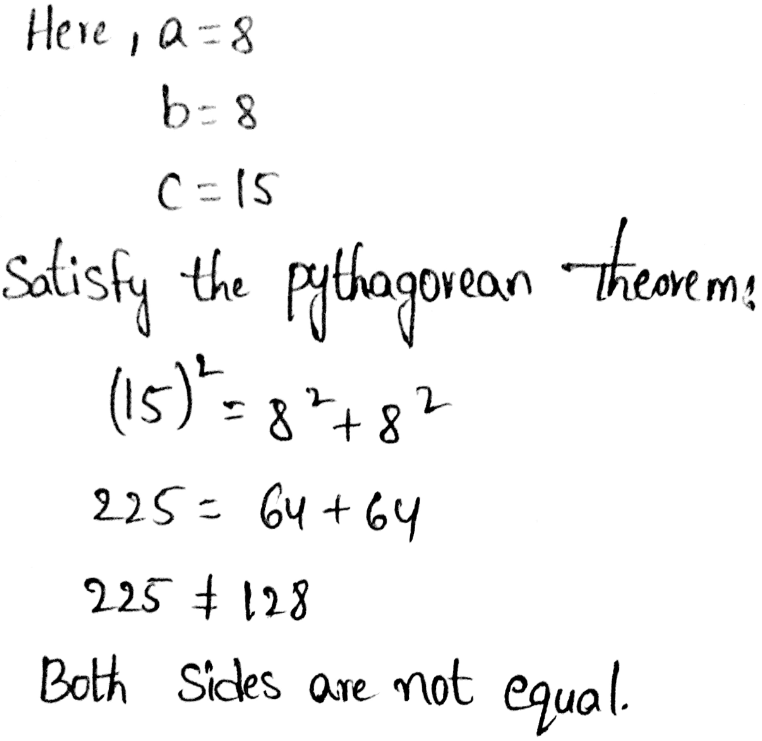
So, the triangle is not the right triangle.
Now, check for triangle 3
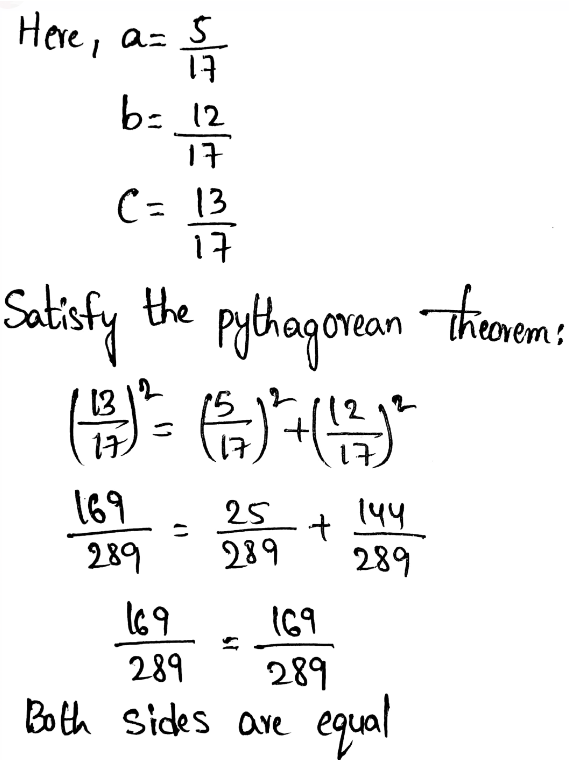
So, the triangle is the right triangle.
Hence, the first and third triangles are right triangles.
Understand The Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Envision Math Grade 8 Solutions
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 392 Exercise 14 Answer
Given:
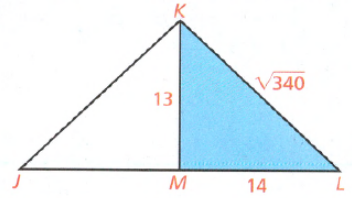
To find whether KM is the height of ΔJKL or not:
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
To know if KM is the height of ΔJKL, it must be perpendicular to JL.
KM is perpendicular to JL, ΔKML must be a right triangle.
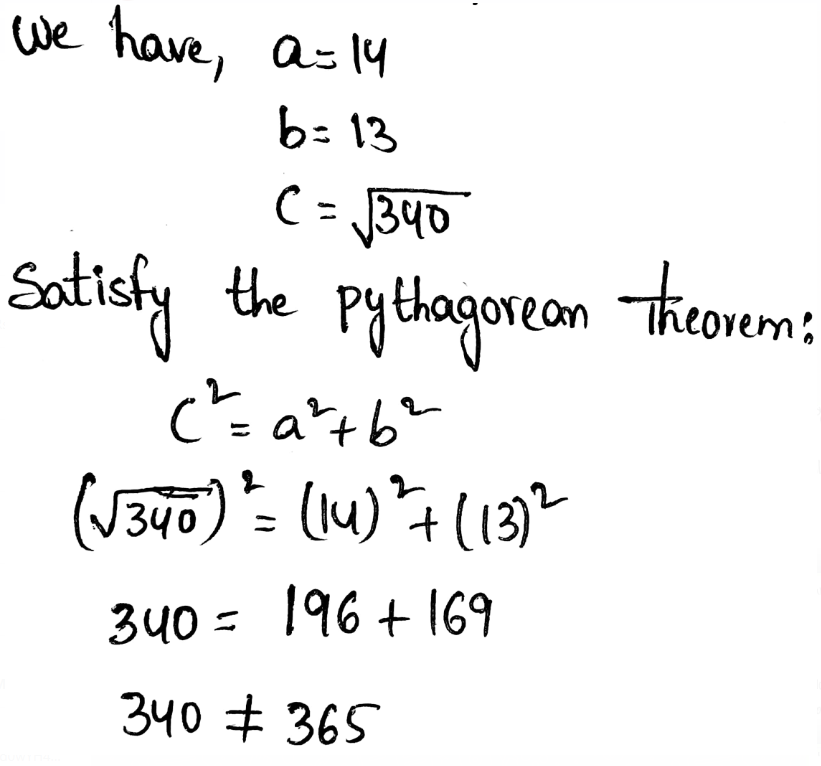
It follows that KM is not perpendicular to JL.
Hence, KM is not the height of ΔJKL using the concept of perpendicular lines and Pythagorean Theorem.
How To Solve Envision Math Grade 8 Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem Problems
Page 392 Exercise 17 Answer
Given:
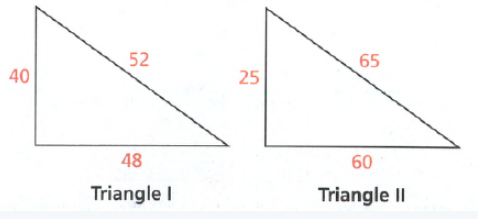
To find which of triangle represents right triangle:
Apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and plug the values.
We have,
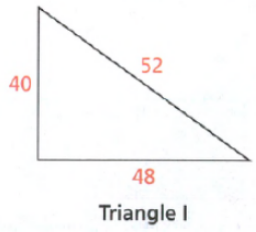
Here, a = 40
b = 48
c = 52
Satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem:
522 = 482 + 402
2704 ≠ 3904
Both sides are not equal.
Hence, it does not represent a right triangle.
We have,
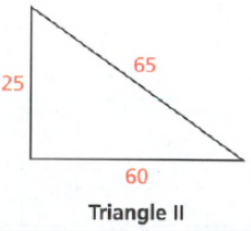
Here, a = 25
b = 60
c = 65
Satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem:
652 = 602 + 252
4225 = 4225
Both sides are equal.
Hence, it represents a right triangle.
Hence, option(B) is correct.
Page 393 Exercise 2 Answer
Given:
ΔPQR has side lengths of 12.5 centimeters,30 centimeters, and 32.5 centimeters
To prove ΔPQR is a right triangle:

Hence, it represents a right triangle.
Hence, proved
Hence, we have proved that ΔPQR is a right triangle.
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 393 Exercise 4 Answer
Given:
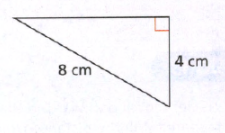
To find: the unknown side length.
Using the Pythagoras equation:
c2 = a2 + b2
where c is hypotenuse of the right triangle whereas ‘a’ and ‘b’ are the other two legs.
Let c be the hypotenuse of the triangle and a and b be the length of the legs of the triangle.
Notice that the hypotenuse and one of the side of the right triangle is given:
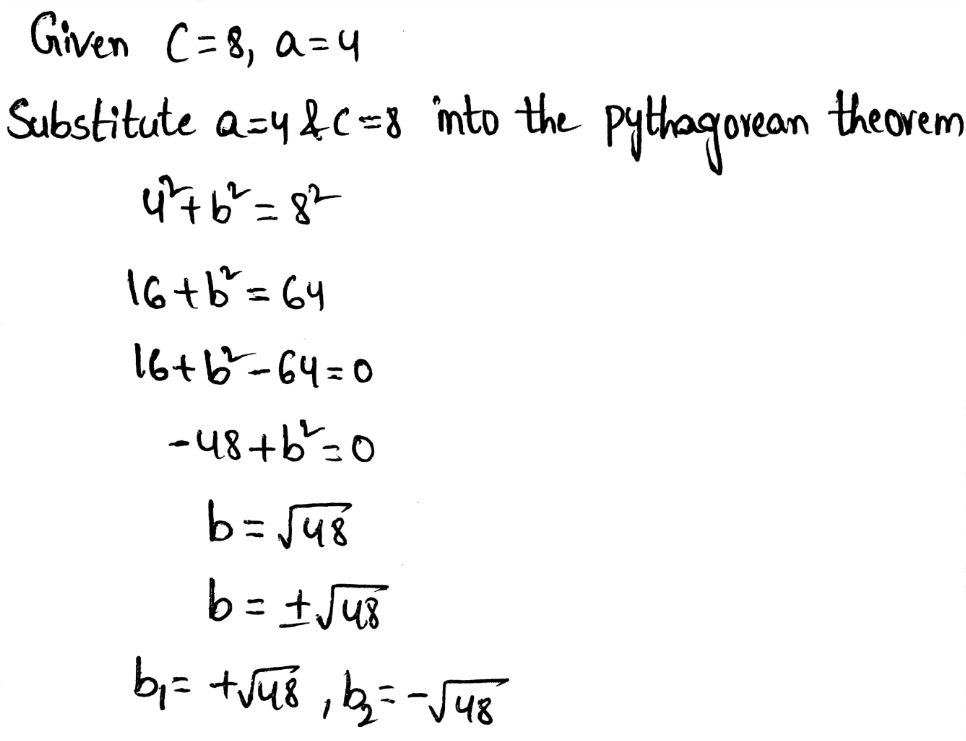
The length of the second leg is 4√3
Free Envision Math Grade 8 Solutions For Exercise 7.1
Page 393 Exercise 5 Answer
Given: The lengths of the legs of a right triangle are 4.5 inches and 6 inches.
To find: the length of the hypotenuse
Using the Pythagoras equation:
c2 = a2 + b2 where c is hypotenuse of the right triangle whereas ‘a’ and ′b’ are the other two legs.
Let a = 4.5 and b = 6 be the legs of a right triangle.
Substitute a = 4.5 and b = 6 to the
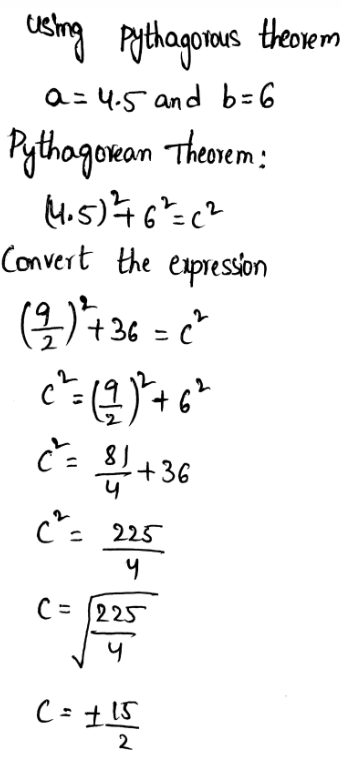
Since the length of the hypotenuse cannot be negative,
therefore, c = 7.5
The length of the hypotenuse is 7.5 inches.
Envision Math Grade 8 Pythagorean Theorem Chapter 7 Worksheet Solutions
Page 393 Exercise 6 Answer
Given: Sides of a triangle
To find: lengths which represent the sides of a right triangle.
Consider 5cm,10cm.15cm
a2 + b2 = c2
Substitute a = 5,b = 10 and c = 15 if the set of numbers is a pythagorean triple.
52 + 102 = 152
L.H.S.= 25 + 100 = 125
R.H.S = 225
therefore, 125 ≠ 225
5cm,10cm.15cm does not represent the sides of a right triangle.
Consider 7 in., 14 in., 25 in.
a2 + b2 = c2
Substitute a = 7,b = 14 and c = 25 if the set of numbers is a pythagorean triple.
72 + 142 = 252
L.H.S.= 49 + 196
= 245
R.H.S = 625
since 245 ≠ 625
7in.,14in.,25in. does not represent the sides of a right triangle.
Consider 13m,84m,85m
a2 + b2 = c2
Substitute a = 13,b = 84 and c = 85 if the set of numbers is a pythagorean triple.
132 + 842 = 852
L.H.S = 169 + 7056
= 7225
R.H.S.= 7225
Since, L.H.S = R.H.S
Therefore, 13m,84m,85m represent the sides of a right triangle.
Consider 5ft,11ft,12ft
a2 + b2 = c2
Substitute a = 5,b = 11 and c = 12 if the set of numbers is a pythagorean triple.
52 + 112 = 122
L.H.S = 25 + 121
= 146
R.H.S.= 144
Since, 146 ≠ 144
therefore, 5ft,11ft,12ft does not represent the sides of a right triangle.
Consider 6ft,9ft,√117ft
a2 + b2 = c2
Substitute a = 6,b = 9 and c = √117 if the set of numbers is a pythagorean triple.
62 + 92 = 117
L.H.S = 36 + 81
= 117
R.H.S = 117
Since, L.H.S = R.H.S
therefore,6ft,9ft,√117ft represent the sides of a right triangle.
Only 13m,84m,85m and 6ft,9ft,√117ft represent the sides of a right triangle.
Solutions For Envision Math Grade 8 Exercise 7.1
Envision Math Grade 8 Volume 1 Chapter 8 Surface Area And Volume Topic 8 Solutions Page 394 Exercise 1 Answer
Given:
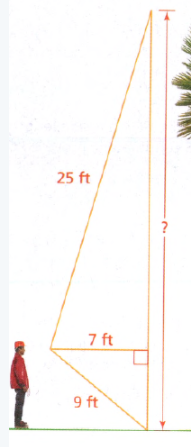
To find: the height of the tree.
Using Pythagoras theorem, we will find the height of the tree.
The height of the tree is the sum of the lengths of the sides BC. and CD, it follows:
h = BC + CD
Notice that the figure is composed of two right triangles △ABC. and △ADC.
Therefore, the length of the sides BC and CD can be determined using the pythagorean Theorem;
a2 + b2 = c2
In the triangle △ABC, the side AB is the hypotenuse.
a2 + b2 = c2
Substitute a = BC, b = AC, and c = AB into the equation:
BC2 + AC2 = AB2
Substitute AC = 7 and AB = 9 into the equation:

Since the length cannot be negative, it follows:
BC ≈ 5.7
Similarly, using the pythagorean theorem, the length of the side CD in the △ADC is 24 .
h = BC + CD
Substitute BC ≈ 5.7 and CD = 24 into the equation:
h ≈ 5.7 + 24
h ≈ 29.7
Therefore, the height of the tree is about 29.7 feet.
Therefore, the height of the tree is about 29.7 feet.
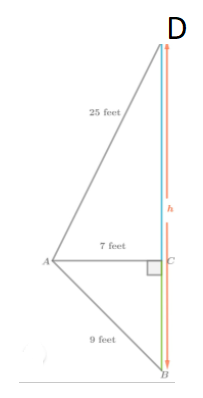
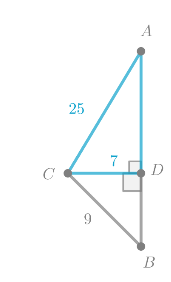
Given:
To find: the height of the tree round to the nearest tenth.
Using pythagoras theorem, we will the height of the tree.
Triangle △BCD is a right triangle.
Substitute BC = 9 and CD = 7 into the Pythagorean Theorem formula, it follows:

Since side length is always positive, it follows:
DB = 4√2
Triangle △ACD is a right triangle.
Substitute AC = 25 and CD = 7 into the Pythagorean Theorem formula, it follows:

Since side length is always positive, it follows:
AD = 24
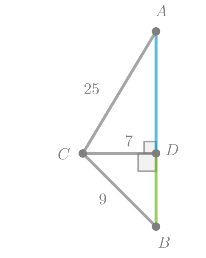
By using the Segment Addition Postulate, it follows:
AB = AD + DB
Substitute AD = 24 and DB = 4√2 into the equation:
AB = 24 + 4√2
The height of the tree is about 29.7ft.
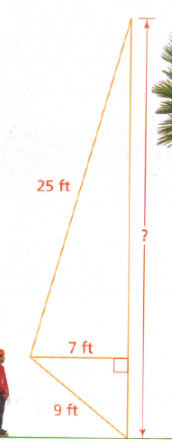
Given: Javier moves backward so that his horizontal distance from the tree is 3 feet greater.
To find: the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree also be 3 feet greater
Use pythagorean theorem.
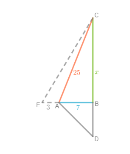
In △ABC, substitute a = 7,b = x and c = 25 in the Pythagorean theorem:

The person moves horizontally 3 feet away from tree to the point E
in △EBC. substitute a = 7+3,b = 24 and c = y in the Pythagorean theorem,
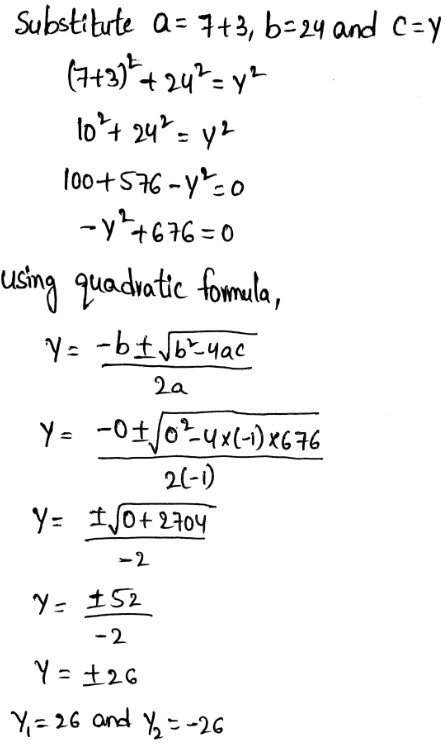
The length can not be negative, therefore the value of y is 26
When the person moves 3 feet horizontally, the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree increase by 1 feet.
This can be concluded by using Pythagorean theorem.
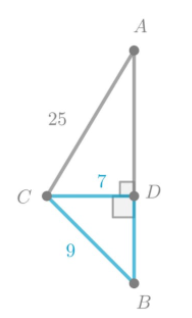
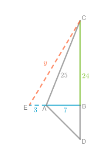
Given: the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree is only 20 feet
To find: Could Javier change his horizontal distance from the tree so that the distance from his eyes to the top of the tree is only 20 feet?
cosθ = \(\frac{\text { base }}{\text { hypotenuse }}\)
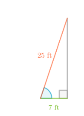
By the definition of cosine:
cosθ = \(\frac{7}{25}\)
When the person moves away from the tree θ decreases which increases value of cosθ
Increase in the value of cosθ decreases the distance from his eyes to top of tree.
cosθ = \(\frac{7}{25}\)
Notice that cosθ is inversely proportional to the distance from person’s eyes to top of tree.
Increase in the value of cosθ decreases the distance from his eyes to top of tree,
At some goint, the distance from his eyes to top of tree can become 20 feet
