Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice
Page 263 Problem 1 Answer
Fill in the blanks of the statements given
A ____________is a mathematical expression involving the sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients.
A Polynomial equation is a mathematical expression involving the sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients.
Page 263 Problem 2 Answer
Fill in the blanks of the statements given-
The ____________ of a polynomial is the greatest variable exponent in the expression.
The Degree of a polynomial is the greatest variable exponent in the expression.
Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 263 Problem 3 Answer
Fill in the blanks of the statements given-
The _______________ states that if the product of two or more factors is equal to zero, then at least one factor must be equal to zero.
The Principle of Zero products states that if the product of two or more factors is equal to zero, then at least one factor must be equal to zero.
Page 264 Problem 4 Answer
m(x)=f(x)+g(x)
f(x)=−1/2x
g(x)=x+5
Predict the family function of m(x)

The family function of m(x) is,
h(x)=x
Hence the family function of m(x) is, h(x)=x the linear function
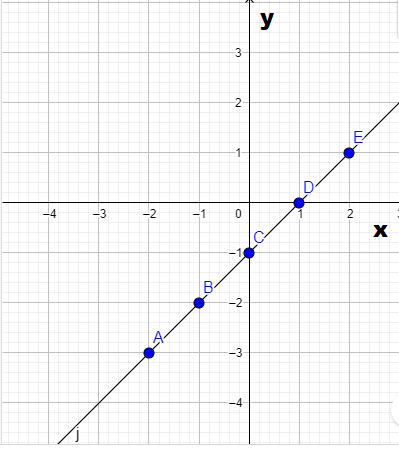
Graph-
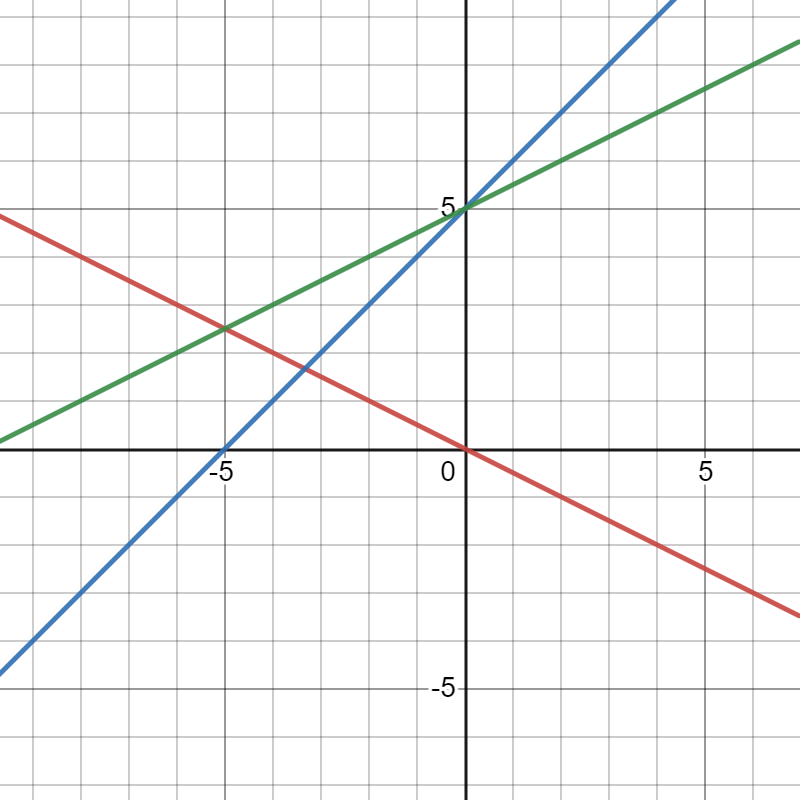
Arnegie Learning Algebra Ii Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Solutions
Page 264 Problem 5 Answer
In the given graph of f(x) and g(x), note the points marked The x values from graph of f(x) and g(x) are (-4, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4)
We know f(x) and g(x) expressionSubstitute the values of x from graph to find m(x)Draw a straight line through the points of m(x) to get graph of m(x).
The function m(x),m(x)=f(x)+g(x)
f(x)=−1/2x
g(x)=x−2
x=(−4,−2,−1,0,1,2,4)
x=−4
m(x)=−1/2(−4)+(−4−2)
=4/2−6
=2−6
m(x)=−4
For x=−2
m(x)=−1/2(−2)+((−2)−2)
=1−4
m(x)=−3
For x=−1
m(x)=−1/2(−1)+((−1)−2)
=1/2−3
m(x)=−2.5
The Function m(x) For x=0
m(x)=−1/2(0)+(0−2)
m(x)=−2
For x=1
m(x)=−1/2(1)+(1−2)
=−1/2−1
m(x)=−1.5
For x=2
m(x)=−1/2(2)+(2−2)
=−2/2
m(x)=−1
For x=4
m(x)=−1/2(4)+(4−2)
=−4/2+2
m(x)=0
The graph of m(x)
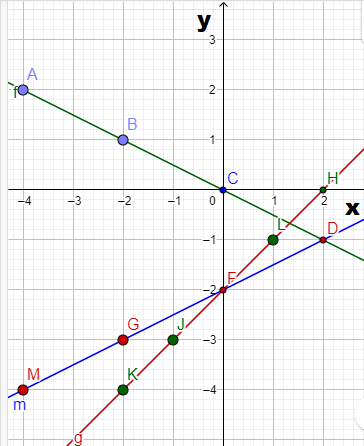
Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 265 Problem 6 Answer
In the given graph of f(x) and g(x), note the points marked The x values from graph of f(x) and g(x) are (-8, -4, -2, 0, 2)
We know f(x) and g(x) expression Substitute the values of x from graph to find m(x)Draw a straight line through the points of m(x) to get graph of m(x).
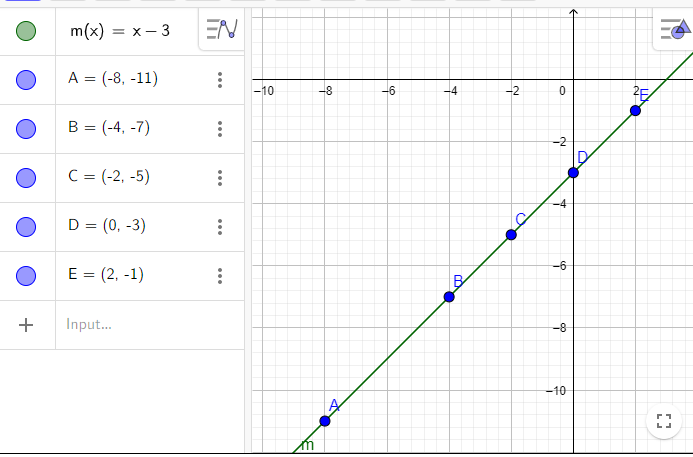
The function m(x)m(x)=f(x)+g(x)
f(x)= 2x
g(x)=−x−3
m(x)=2x−x−3
m(x)=x−3
The m(x) for x value -8 and -4m(x)=x−3
for x=−8
m(x)=−8−3
m(x)=−11
for x=−4
m(x)=−4−3
m(x)=−7
The m(x) for x values -2, 0 and 2m(x)=x−3
for x=−2
m(x)=−2−3
m(x)=−5
for x=0
m(x)=0−3
m(x)=−3
for x=2
m(x)=2−3
m(x)=−1
The graph of m(x) with points (-8,-11), (-4,-7), (-2,-5), (0,-3) and (2,-1)
The graph of m(x),f(x) and g(x)
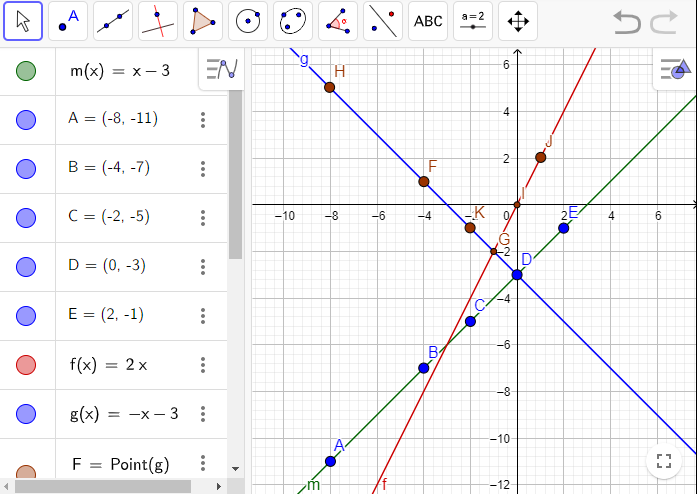
Page 263 Problem 7 Answer
Find the value of k(x) and h(x) for given x values from given graph
To find j(x), Subtract h(x) from k(x)Complete the table by finding j(x) for each x givenMark the results in graph
The table of h(x) and j(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | -2 | -5 | |
| -1 | -1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | -1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 2 | 3 |
The complete table
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | -2 | =-5-(2)=-3 | -5 |
| -1 | -1 | =-3-(-1)=-2 | -3 |
| 0 | 0 | =-1-(0)=-1 | -1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1-1=0 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 3-2=1 | 3 |
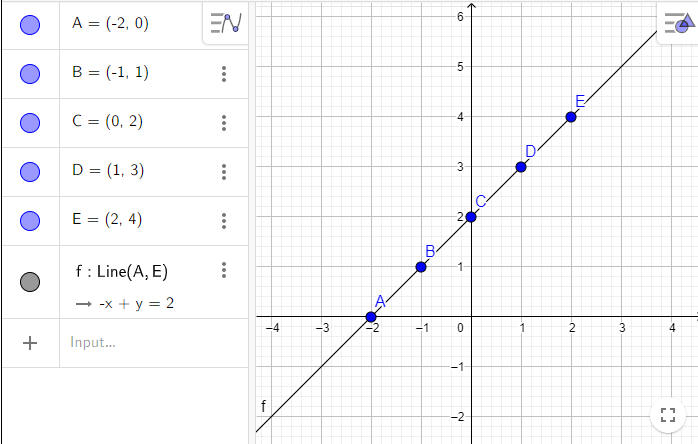
The graph of j(x)
Skills Practice Exercise 1.5 Answers
Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 266 Problem 8 Answer
Find the value of k(x) and h(x) for given x values from given graph
To find j(x), Subtract h(x) from k(x)Complete the table by finding j(x) for each x givenMark the results in graph
The table for h(x) and k(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)-j(x) |
| -2 | -4 | -4 | |
| -1 | -2 | -1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | |
| 2 | 4 | 8 |
The complete table
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)-j(x) |
| -2 | -4 | =-4-(-4)=0 | -4 |
| -1 | -2 | =-1-(-2)=1 | -1 |
| 0 | 0 | 2-0=2 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 4-2=3 | 5 |
| 2 | 4 | 8-4=4 | 8 |
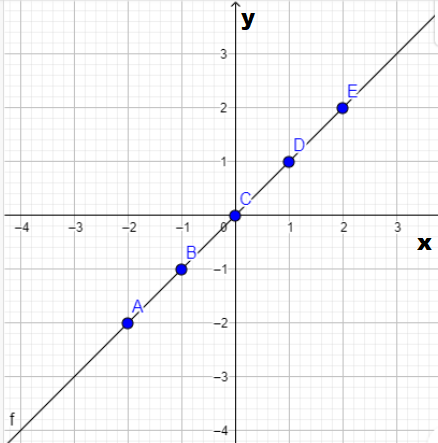
The graph of j(x)
Page 266 Problem 9 Answer
Find the value of k(x) and h(x) for given x values from given graph
To find j(x), Subtract h(x) from k(x)Complete the table by finding j(x) for each x givenMark the results in graph
The table for h(x) and k(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 6 | -6 | |
| -1 | 3 | -4 | |
| 0 | 0 | -2 | |
| 1 | -3 | 1 | |
| 2 | -6 | 2 |
The complete table
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 6 | =-6-6=-12 | -6 |
| -1 | 3 | =-4-3=-7 | -4 |
| 0 | 0 | =-2-0=-2 | -2 |
| 1 | -3 | 1-(-3)=4 | 1 |
| 2 | -6 | 2-(-6)=8 | 2 |
The graph of j(x)

Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 267 Problem 10 Answer
Find the value of k(x) and h(x) for given x values from given graph
To find j(x), Subtract h(x) from k(x)Complete the table by finding j(x) for each x givenMark the results in graph
The table for h(x) and k(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 4 | 2 | |
| -1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 2 | 4 | 6 |
The complete table
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 4 | -2 | 2 |
| -1 | 1 | -1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 | 6 |
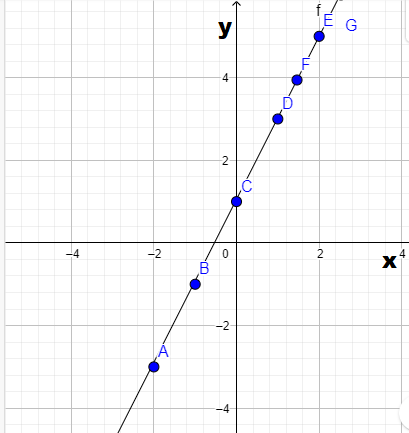
The graph of j(x)
Page 267 Problem 11 Answer
Find the value of k(x) and h(x) for given x values from given graph
To find j(x), Subtract h(x) from k(x)Complete the table by finding j(x) for each x givenMark the results in graph
The table for h(x),k(x) and j(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 2 | -3 | |
| -1 | 2 | -1 | |
| 0 | 2 | 1 | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 2 | 2 | 5 |
The complete table
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 2 | =-3-2=-5 | -3 |
| -1 | 2 | =-1-2=-3 | -1 |
| 0 | 2 | 1-2=-1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 3-2=1 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 | 5-2=3 | 5 |
The graph of j(x)
Algebra Ii Chapter 1 Skills Practice Solutions Exercise 1.5
Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 267 Problem 12 Answer
Find the value of k(x) and h(x) for given x values from given graph
To find j(x), Subtract h(x) from k(x)Mark the results in graph Complete the table after finding j(x) for each x given
The value of h(x) and k(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 4 | 10 | |
| -1 | 2 | 6 | |
| 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 2 | 4 | 6 |
To find j(x)
| x | h(x) | j(x) | k(x)=h(x)+j(x) |
| -2 | 4 | 10-4=6 | 10 |
| -1 | 2 | 6-1=5 | 6 |
| 0 | 0 | 4-0=4 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 4-1=3 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | 6-4=2 | 6 |
The graph of j(x)
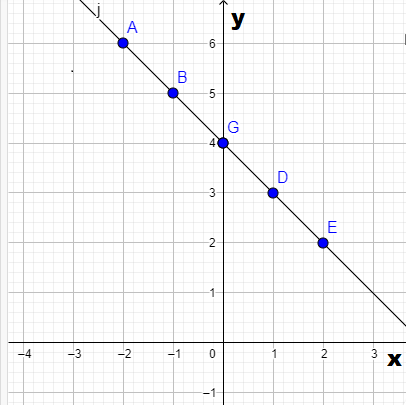
Page 268 Problem 13 Answer
Given- The three polynomial functions,h(x)=−3x+5
j(x)=−5x−7
k(x)=−8x−2
To find- To show that h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
We will first, add the functions h(x) and j(x), then compare the result with the function k(x) to show that they are equivalent.
The given functions are,
h(x)=−3x+5
j(x)=−5x−7
k(x)=−8x−2
Now,h(x)+j(x)=−3x+5+(−5x−7)
=−3x+5−5x−7
=−8x−2
And,k(x)=−8x−2
We know that two polynomials are equivalent if they have equal coefficients of corresponding powers of the independent variable.
∴h(x)+j(x)=k(x)
So,h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
On adding the functions h(x) and j(x), we get the value that is the same as the function k(x).
So, the function h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x)
Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 268 Problem 14 Answer
Given- The three polynomial functions,h(x)=1/2x+9
j(x)=1/2x+6
k(x)=x+15
To find- To show that h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
We will first, add the functions h(x) and j(x), then compare the result with the function k(x) to show that they are equivalent.
The given functions are,
h(x)=1/2x+9
j(x)=1/2+6
k(x)=x+15
Now,h(x)+j(x)=1/2
x+9+1/2
x+6
=1/2x+1/2x+9+6
=x+15
And,k(x)=x+15 We know that two polynomials are equivalent if they have equal coefficients of corresponding powers of the independent variable.
∴h(x)+j(x)=k(x)
So,h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
On adding the functions h(x) and j(x), we get the value that is the same as the function k(x).
So, the function h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x)
Carnegie Learning Skills Practice Exercise 1.5 Explained
Carnegie Learning Algebra II Student Skills Practice 1st Edition Chapter 1 Exercise 1.5 Skills Practice Page 268 Problem 15 Answer
Given- The three polynomial functions,h(x)=−12x−1
j(x)=−7x+11
k(x)=−19x+10
To find- To show that h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
We will first, add the functions h(x) and j(x), then compare the result with the function k(x) to show that they are equivalent.
The given functions are,
h(x)=−12x−1
j(x)=−7x+11
k(x)=−19x+10
Now,h(x)+j(x)=−12x−1+(−7x+11)=−12x−1−7x+11
=−19x+10
And,k(x)=−19x+10
We know that two polynomials are equivalent if they have equal coefficients of corresponding powers of the independent variable.
∴h(x)+j(x)=k(x)
So,h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
On adding the function h(x) and j(x), we get the value that is the same as the function k(x).
So, the function h(x)+j(x) is equivalent to k(x).
